Maintaining the right body temperature is crucial for our overall health and well-being. Our bodies are designed to regulate temperature through a complex system of thermoregulation. However, certain health conditions can disrupt this balance, leading to high body heat.
Importance of maintaining the right body temperature
The human body is a remarkable system that functions optimally within a narrow range of temperatures. Maintaining the ideal body temperature is crucial for overall health and well-being. There are both pros and cons in maintaining body temperature and the benefits far outweigh the potential drawbacks.
The pros of maintaining optimal body temperature are as follows.
Homeostasis and Metabolic Function
Maintaining an optimal body temperature allows the body to achieve homeostasis, the state of internal balance. It enables efficient metabolic function, ensuring that essential biochemical reactions occur at the appropriate rates. This enables cells to carry out their functions effectively, promoting overall health.
Improved Immune System
Optimal body temperature supports a robust immune system. An elevated body temperature, commonly known as a fever, is a natural defence mechanism that helps the body fight off infections. It stimulates immune cells, enhances their activity, and accelerates the production of antibodies, thereby aiding in the elimination of pathogens.
Enhanced Cognitive Performance
Body temperature has a direct impact on cognitive function. Maintaining the ideal temperature range optimizes neural activity, facilitating better cognitive performance, focus, and memory. It promotes faster information processing and decision-making abilities.
Efficient Physical Performance
During physical activities, maintaining an optimal body temperature is crucial for peak performance. The body regulates temperature through sweating, which cools the skin as moisture evaporates. By preventing overheating, maintaining body temperature optimizes energy expenditure and endurance, allowing individuals to perform at their best.
The Cons of Maintaining Optimal Body Temperature
Energy Expenditure
Maintaining optimal body temperature requires energy expenditure. The body expends additional calories to generate heat or cool down, depending on environmental conditions. In extreme temperatures, the body may need to work harder, potentially leading to increased fatigue and decreased energy levels.
Vulnerability to Extreme Temperatures
While the body has mechanisms to regulate temperature, it is not immune to extreme heat or cold. Long term exposure to high or low temperatures can strain the body’s thermoregulatory system, leading to heatstroke or hypothermia, respectively. It is crucial to protect oneself adequately in extreme conditions to prevent adverse health effects.
Disruption of Sleep Patterns
Temperature plays a vital role in regulating sleep patterns. If the room temperature is too low or high, it can disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to difficulties falling asleep or maintaining restful sleep. This can result in fatigue, impaired cognitive function, and other health issues.
Individual Variations and Health Conditions
Different individuals may have varying tolerances to temperature changes. Some may be more sensitive to heat, while others may be more sensitive to cold. Additionally, certain medical conditions like thyroid disorders or cardiovascular diseases, can affect the body’s ability to regulate temperature effectively.
Maintaining optimal body temperature is essential for overall health and well-being. The benefits of temperature regulation, including homeostasis, improved immune system function, enhanced cognitive performance, and efficient physical performance, far outweigh the potential drawbacks. While energy expenditure and vulnerability to extreme temperatures may pose challenges, it is crucial to protect oneself adequately and adapt to environmental conditions. Understanding the importance of maintaining optimal body temperature empowers individuals to prioritize their well-being and make informed decisions for a healthy lifestyle.
What health conditions can increase body heat?
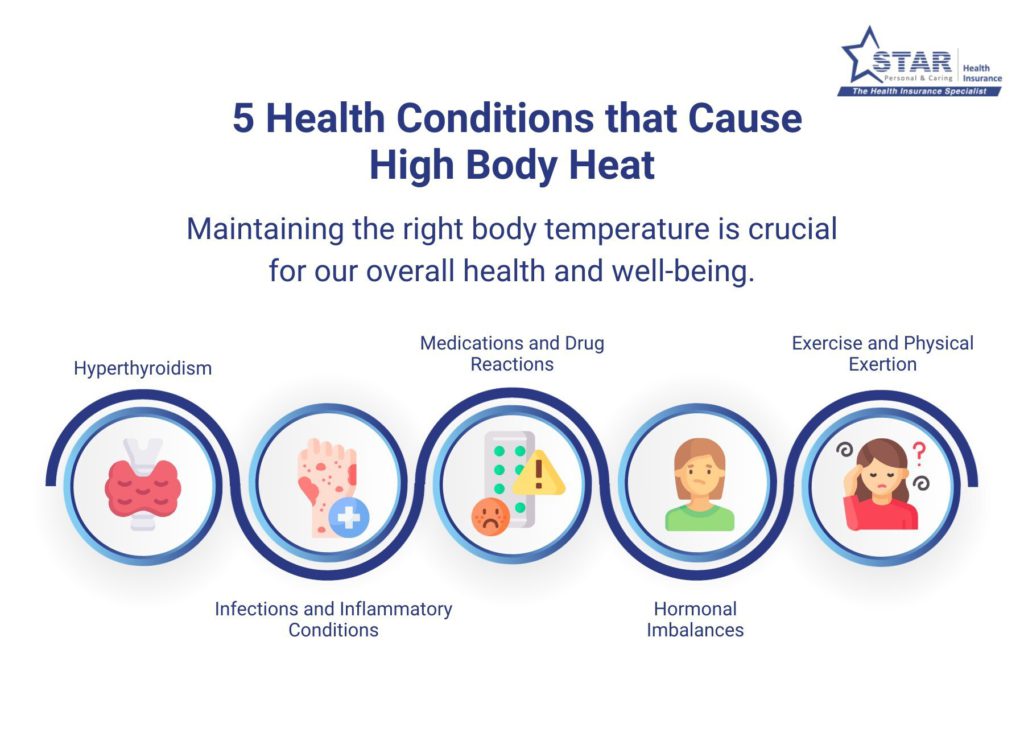
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a health condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, which produces an excess amount of thyroid hormones. These hormones are responsible for regulating metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature.
Individuals with hyperthyroidism may experience symptoms such as excessive sweating, heat intolerance, increased heart rate, weight loss, and anxiety. Treatment options for hyperthyroidism include medication to regulate thyroid hormone levels, radioactive iodine therapy, or in rare cases, surgical procedures are performed to remove the thyroid gland. Managing stress levels and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also help control symptoms.
Infections and Inflammatory Conditions
Certain infections and inflammatory conditions can cause elevated body temperature. Infections such as urinary tract infections, cellulitis and pneumonia can trigger an immune response in the body, leading to inflammation and an increase in body heat.
Symptoms associated with infections and inflammatory conditions include fever, chills, fatigue, muscle aches, and localized pain or redness. Treatment typically involves addressing the underlying infection through antibiotics, antiviral medications, or other appropriate treatments based on the specific condition.
It is crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment, as untreated infections can lead to complications and further health issues.
Medications and Drug Reactions
Certain medications can cause elevated body temperature as a side effect. Stimulant medications that are used to treat mental health problems like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, can increase metabolism and raise body heat. Antidepressants, antipsychotics, and some antibiotics may also contribute to higher body temperatures.
In addition to medications, drug interactions can also impact body temperature regulation. Combining certain medications or using them alongside illicit substances can lead to an imbalance in the body’s thermoregulatory system, resulting in increased body heat.
If you notice persistent high body heat while taking medications, it is crucial to consult your healthcare provider. They can review your medication regimen, adjust dosages if necessary, or explore alternative options to minimize side effects.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the body’s temperature regulation mechanisms. Such imbalances occur during pregnancy or menopause. Menopause is a transition in a woman’s life when the ovaries produce fewer hormones, including estrogen. The decline in hormone level in the body can cause night sweats and increased body heat.
Adrenal gland disorders, such as Cushing’s syndrome or adrenal insufficiency, can also impact body temperature regulation. These conditions affect the production of hormones, including cortisol, which plays a role in managing stress and regulating metabolism.
Treatment options for hormonal imbalances may include hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle modifications, and stress management techniques. Consulting with a healthcare professional is vital to determine the underlying cause of the imbalance and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Exercise and Physical Exertion
Engaging in intense physical activity can temporarily increase body heat due to increased metabolic rate and muscle exertion. During exercise, our bodies produce heat as a byproduct of energy production. This excess heat needs to be dissipated to maintain a stable body temperature.
However, if the body’s cooling mechanisms, such as sweating and vasodilation, are not sufficient to regulate body heat, it can lead to overheating and potentially heat-related illnesses.
Heat-related illnesses, such as dehydration, heat exhaustion or heat stroke occurs when the body can’t dissipate heat adequately. Symptoms of heat exhaustion include sweating, dizziness, nausea, headache, weakness and an elevated body temperature. Heatstroke, a more severe condition, can lead to a dangerously high body temperature, altered mental state, rapid heartbeat, and even organ failure.
To prevent overheating during exercise, it’s essential to take certain precautions. Stay hydrated by drinking enough water before and after physical activity. Wear lightweight and breathable clothing and choose the appropriate time of day for outdoor exercise, avoiding the hottest hours.
Listen to your body and recognize the warning signs of overheating. If you experience symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, or nausea, take a break, move to a cooler environment, and hydrate.
To minimize the risks of developing health conditions that increase body temperature, you can follow these guidelines:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Adopt a balanced diet that includes lean meat, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts. Limit your intake of processed or refined foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of sodium. Engage in physical activities and maintain a healthy weight.
Stay hydrated: Drink enough water throughout the day to prevent dehydration. Fluids help regulate body temperature and support overall health. Avoid excessive consumption of caffeinated, sugary or alcoholic beverages, as they can contribute to dehydration.
Be mindful of your environment: Avoid spending prolonged periods in extreme heat or cold environments. In hot weather, stay in shaded areas, wear loose-fitting, lightweight clothing, and use sunscreen. In cold weather, dress warmly in layers and protect your extremities from frostbite.
Practice good hygiene: Personal hygiene is important when it comes to maintaining good health. Wash your hands frequently to reduce the risk of infections that can elevate body temperature. Maintain cleanliness in your living environment and avoid close contact with individuals who are sick.
Manage stress: Stress can have a negative impact on your overall health. Find ways to cope with stress, such as engaging in relaxation techniques, practising mindfulness or meditation, and participating in activities you enjoy.
Get regular check-ups: Visit a doctor or a healthcare provider for routine check-ups and screenings. Regular medical examinations can help detect and manage any underlying health conditions that may contribute to an increased body temperature.
Be cautious with medications and supplements: Some medications and supplements can affect body temperature. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and inform them of any medications or supplements you are taking.
Take appropriate precautions during illness: If you have a fever or are experiencing symptoms of an illness, take appropriate measures to manage your condition. Follow your healthcare provider’s advice, rest, and stay hydrated.
These guidelines are general recommendations. If you have specific concerns or underlying health conditions, it is important to consult with your doctor for personalized advice and guidance.
Conclusion
High body heat can be caused by various health conditions, including hyperthyroidism, infections, inflammatory conditions, medication side effects, hormonal imbalances, and physical exertion. Recognizing the symptoms associated with these conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
If you experience persistent high body heat or other concerning symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, order necessary tests, and develop a personalized treatment plan based on the underlying cause.
Everyone’s situation is unique, and a healthcare professional can provide the most accurate guidance tailored to your specific needs.
By understanding the potential causes of high body heat and seeking appropriate medical care, you can work towards maintaining optimal body temperature regulation and overall health. Stay proactive in taking care of your well-being and prioritize your body’s temperature balance.
FAQ’s
Is high body temperature normal?
The average normal body temperature is generally accepted as 98.6°F. The normal body temperature can range between 97°F to 99°F. A temperature over 100.4°F indicates sickness or fever.
What causes high body heat?
Various health conditions like
1. Hypothyroidism
2. Infections
3. Inflammation
4. Physical activities
5. Medication reactions and
6. Hormonal imbalances can cause high body heat.
What is the normal body temperature range?
The “normal” body temperature can range between 97°F to 99°F. For most people, the average normal body temperature is usually around 98.6°F.
DISCLAIMER: THIS BLOG/WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE
The Information including but not limited to text, graphics, images and other material contained on this blog are intended for education and awareness only. No material on this blog is intended to be a substitute for professional medical help including diagnosis or treatment. It is always advisable to consult medical professional before relying on the content. Neither the Author nor Star Health and Allied Insurance Co. Ltd accepts any responsibility for any potential risk to any visitor/reader.





